- 1.
- A rotation is positive when the reference frame rotates anticlockwise as seen looking towards the origin from the positive region of the specified axis.
- 2.
- The characters of ORDER define which axes the three successive rotations are about. A typical value is `ZXZ', indicating that RMAT is to become the direction cosine matrix corresponding to rotations of the reference frame through PHI radians about the old z-axis, followed by THETA radians about the resulting x-axis, then PSI radians about the resulting z-axis.
- 3.
- The axis names can be any of the following, in any order or
combination: X, Y, Z, uppercase or lowercase, 1, 2, 3. Normal
axis labelling/numbering conventions apply; the xyz (
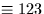 ) triad is right-handed. Thus, the `ZXZ' example given above
could be written `zxz' or `313' (or even `ZxZ' or `3xZ'). ORDER
is terminated by length or by the first unrecognized character.
Fewer than three rotations are acceptable, in which case the later
angle arguments are ignored. Zero rotations produces a unit RMAT.
) triad is right-handed. Thus, the `ZXZ' example given above
could be written `zxz' or `313' (or even `ZxZ' or `3xZ'). ORDER
is terminated by length or by the first unrecognized character.
Fewer than three rotations are acceptable, in which case the later
angle arguments are ignored. Zero rotations produces a unit RMAT.
